Introduction
In a data-driven economy, access to real-time, accurate, and comprehensive information can define a business’s competitive edge. Web scraping—automatically extracting data from websites—has become one of the most powerful tools for collecting public online data. When combined with Artificial Intelligence (AI), scraping becomes more efficient, scalable, and insightful, giving rise to what we now call AI-Powered Scraping.
However, the intersection of AI Web Scraping and data ethics introduces important ethical and legal considerations that businesses must not ignore. From respecting user consent to complying with data protection laws, companies need to tread carefully.
This blog explores how businesses can responsibly harness AI-Powered Scraping for large-scale data collection while adhering to Ethical Web Scraping standards and legal frameworks. From consent to compliance, we’ll break down the principles, practices, and pitfalls associated with ethical AI Web Scraping—ensuring your strategy is both powerful and principled.
Understanding the Basics - What Is AI-Driven Web Scraping?

Web scraping is the automated technique of extracting data from websites, often used to collect publicly available information at scale. Traditional scraping methods rely on static rules or scripts, which can be fragile when websites change layouts. With the rise of AI-Powered Scraping, this process has evolved dramatically. By incorporating machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision, Web Scraping with AI can intelligently navigate complex web structures, understand context, and extract relevant data more accurately and efficiently.
AI-driven scraping enables systems to interpret unstructured or semi-structured data, such as product descriptions, user reviews, or news articles. It can identify patterns, automate data labeling, summarize insights, and even adapt to changes in website structure over time without manual reprogramming.
Common Use Cases in Business:
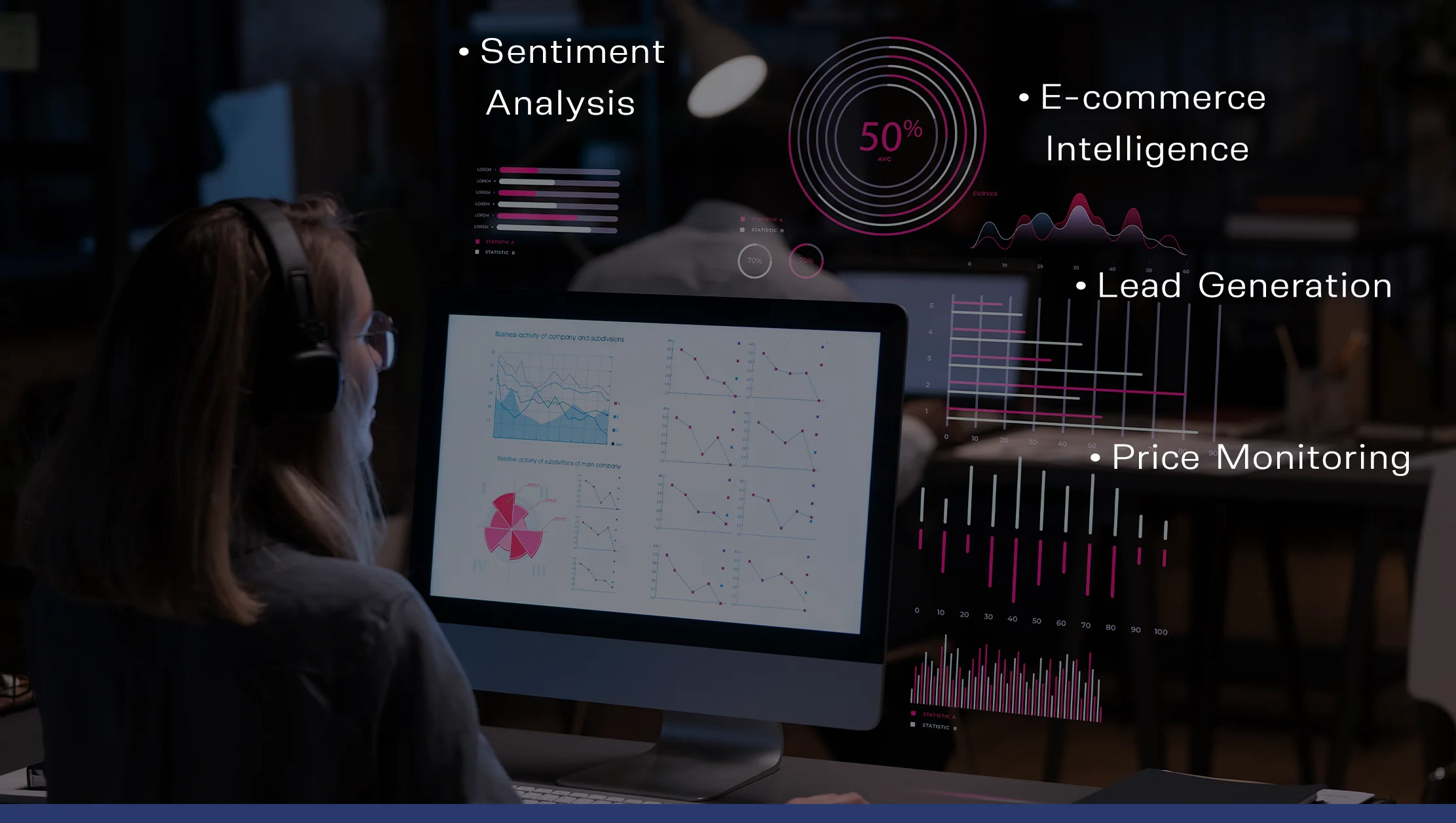
- Price Monitoring: Track competitor pricing in real-time to adjust your strategies dynamically.
- Sentiment Analysis: Analyze customer reviews across platforms for actionable product and service feedback.
- News Aggregation: Collect brand mentions or market updates for PR and crisis management.
- Lead Generation: Extract business contact information from directories or platforms like LinkedIn.
- E-commerce Intelligence: Monitor product listings, inventory levels, and promotional campaigns.
Despite its immense value, businesses must also consider the ethical implications. Ethical Data Scraping goes beyond legality—it's about respecting digital boundaries, user privacy, and terms of service. Implementing Ethical Web Data Extraction and Ethical Data Mining practices ensures data is collected transparently, securely, and in compliance with local regulations.
As AI makes scraping smarter, the responsibility to keep it fair and lawful also grows. Businesses must adopt a forward-thinking mindset, combining innovation with integrity to responsibly harness the full potential of AI-Powered Scraping.
The Ethical Dilemma - Why Does Responsible Scraping Matter?

AI scraping is powerful, but power must be wielded responsibly. Unethical scraping practices can lead to:
- Data breaches
- IP infringement
- Loss of consumer trust
- Legal consequences under data protection laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA)
Key Ethical Questions Businesses Should Ask:
- Is the data being scraped publicly accessible?
- Are there any terms of service (ToS) prohibiting scraping?
- Does the scraping respect site structure and bandwidth (i.e., does it avoid disrupting the host server)?
- Are personal or sensitive data involved?
- Is user consent obtained when required?
Failing to consider these aspects can lead to reputational and financial damage—even if your intentions are good.
Choose responsible scraping to protect your brand, build trust, and ensure long-term compliance—because ethical data collection is a smart and sustainable business strategy.
Get Insights Now!Legal Landscape - What Laws Govern Web Scraping?

The legality of scraping varies by jurisdiction and context. Here are some of the major regulations to be aware of:
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation - EU)
- Personal data must be collected with consent.
- Data subjects have the right to be informed and forgotten.
- Scraping identifiable personal data without clear legal grounds is a violation.
CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)
- Gives consumers the right to know what data is collected and request its deletion.
- Unauthorized data scraping of personal information can lead to penalties.
Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA - US)
- Accessing a computer system “without authorization” can be a criminal offense.
- Courts vary on whether scraping publicly accessible websites violates the CFAA.
Best Practices for Ethical AI Scraping

Ethical scraping is not just about staying within legal boundaries—it’s about building trust, maintaining transparency, and ensuring long-term business sustainability. By following these Web Scraping Best Practices, businesses can responsibly leverage the power of AI-Powered Scraping without compromising ethics or user trust.
a. Respect Robots.txt Files
The robots.txt file specifies what parts of a website are off-limits to scrapers. Following it is a key element of Legal Web Scraping. Always check and honor this file before initiating any scraping activity.
b. Monitor Your Scraping Load
While AI enables scraping at scale, excessive requests can crash servers and affect real users. Implement throttling, random delays, and respectful frequency limits to maintain ethical standards and server health.
c. Attribute Sources Where Required
When redistributing scraped content like reviews or articles, always provide proper attribution. This supports Data Ethics in AI and is often a legal requirement, especially when dealing with intellectual property.
d. Filter Out Personal Data
Ethical AI tools should identify and exclude personally identifiable information (PII) such as names, emails, and addresses unless consent is explicitly provided. This practice is essential for Legal Web Scraping and ensures GDPR or similar regulation compliance.
e. Use AI for Data Cleaning, Not Intrusion
AI should be used to clean and analyze publicly available structured data. Avoid scraping password-protected areas, user profiles, or private content—these actions are both unethical and potentially illegal.
f. Maintain Transparency
If your AI scraping tools collect data that impacts consumers—like product reviews or job listings—disclose your data sources and scraping methods. Transparency reinforces ethical behavior and builds credibility.
By integrating Data Ethics in AI into your scraping strategies, businesses can innovate responsibly while preserving user trust and regulatory compliance.
Follow ethical AI scraping practices to ensure compliance, protect user privacy, and gain reliable insights—build data strategies that are both powerful and principled.
Get Insights Now!Ethical AI Considerations Beyond the Scraping Itself

When businesses adopt AI-Powered Scraping, ethical responsibility doesn’t stop at how the data is collected—it extends to how that data is used, processed, and interpreted by AI models. Particularly with large language models (LLMs) and predictive systems, the quality, fairness, and diversity of the training data have a direct impact on the outcomes. This makes it critical to go beyond simple AI scraping compliance and address broader ethical concerns.
Bias Minimization
One of the most common challenges in Responsible AI in Data Collection is bias. If your web scraping activities focus only on a narrow range of sources—such as specific regions, languages, or demographic groups—your AI models may develop biased outputs. To avoid this, businesses should use diverse datasets, continuously audit their scraping sources, and implement fairness checks to ensure balanced representation.
Explainability
It’s important that businesses are transparent about how scraped data is used in AI decision-making. This means being able to clearly explain how certain inputs from web scraping contribute to specific outputs or predictions. Explainability not only helps build trust with users but also ensures alignment with Web Scraping GDPR requirements, where users may have the right to understand automated decisions affecting them.
Accountability
Ethical scraping should be institutionalized as part of your compliance or data governance framework. Designate internal ownership for data practices, including documentation, auditing, and adherence to AI scraping compliance policies. This promotes a culture of accountability and ensures that your organization is aligned with global standards on Responsible AI in Data Collection.
By addressing these deeper ethical layers, businesses can build more trustworthy AI systems that are both powerful and principled.
Real-World Case Studies: Ethical and Unethical Scraping
Case 1: LinkedIn vs. hiQ Labs

hiQ Labs used AI-Powered Scraping to extract data from publicly visible LinkedIn profiles for employee analytics. LinkedIn sued, citing violations of the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA), arguing that hiQ's access, though public, was unauthorized. The court initially sided with hiQ, but the case raised serious concerns about the difference between “public data” and “authorized data use.”
Lesson: Even publicly accessible data may carry implied terms of use. For Ethical Web Scraping, always read terms and conditions and obtain permissions when in doubt.
Case 2: Common Crawl

Common Crawl, a non-profit, ethically collects vast amounts of web data for open research and model training. It respects robots.txt instructions and scrapes only openly licensed or public content. The data is widely used in AI Web Scraping and LLM training, such as GPT models, because of its transparent and lawful collection methods.
Lesson: Transparency, respect for site permissions, and a focus on public benefit are hallmarks of Ethical Web Scraping and make for sustainable long-term strategies.
Case 3: Price Monitoring in E-Commerce
Many online retailers use AI-Powered Scraping tools to monitor competitor pricing. Businesses that respect platform policies, limit scraping frequency, and attribute data sources typically avoid legal issues. However, aggressive scrapers ignoring site terms have faced legal notices and blacklisting.
Lesson: AI Web Scraping must balance performance with respect for digital boundaries. Scraping at scale is acceptable when conducted ethically and within legal parameters.
These cases show that the difference between ethical and unethical AI-Powered Scraping often lies in intent, transparency, and respect for platform guidelines.
Future Outlook: What’s Next for AI Scraping Ethics?

As AI advances, scraping is becoming more complex—and so is the ethical landscape.
Emerging Trends:
- Synthetic Data Generation: AI can generate pseudo-real data for testing instead of scraping sensitive content.
- Federated Learning: AI models trained on decentralized data, reducing the need for mass scraping.
- AI Governance Frameworks: More companies will adopt internal AI ethics guidelines.
- AI Detection of Scrapers: Websites are using AI to detect and block unethical bots, increasing the need for transparency and compliance.
Businesses must future-proof their scraping strategies with adaptable ethical guidelines.
Conclusion
AI-driven web scraping offers enormous potential for innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage. But with this power comes a clear responsibility. Businesses must approach data extraction through the lens of Ethical Web Scraping—not just to remain compliant with regulations like GDPR and CCPA, but to safeguard user trust and protect brand reputation in the long run.
By integrating AI-Powered Scraping with transparency, legal diligence, and respect for digital boundaries, organizations can unlock valuable insights while maintaining ethical standards. Following best practices in AI Web Scraping ensures that data collection is not only effective but also principled, secure, and sustainable.
At Real Data API, we believe Ethical Web Scraping isn’t a limitation—it’s a long-term strategic advantage. Our scraping solutions are designed with compliance, security, and transparency at their core, empowering businesses to leverage AI-Powered Scraping for smarter, more responsible decision-making.